Out Of This World Info About How To Diagnose Mastocytosis

Mastocytosis has a set of standard diagnostic testing.
How to diagnose mastocytosis. In all patients with sm, bone densitometry should be included in the diagnostic work up and repeated periodically to detect early osteoporosis. Among the extracutaneous sites, gastrointestinal tract is often affected, but nonspecific clinical manifestations combined with subtle histological findings of the disease makes the diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and examine your skin.
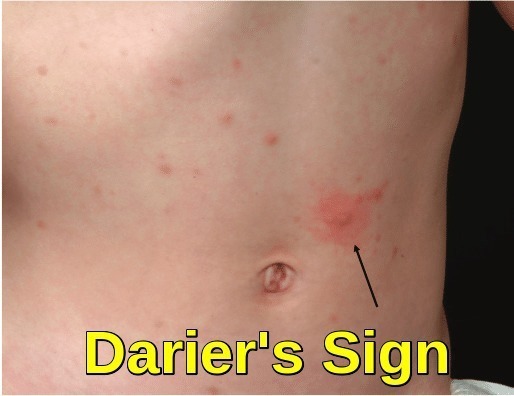
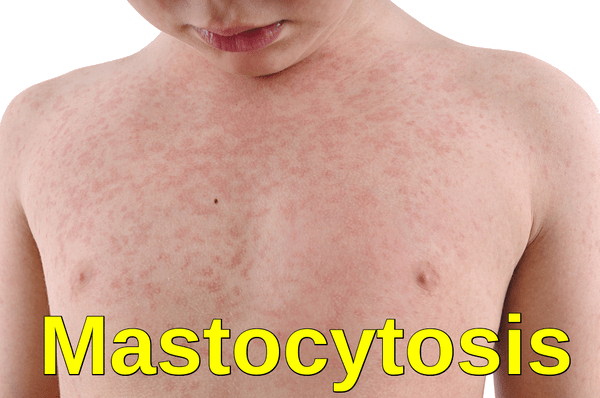
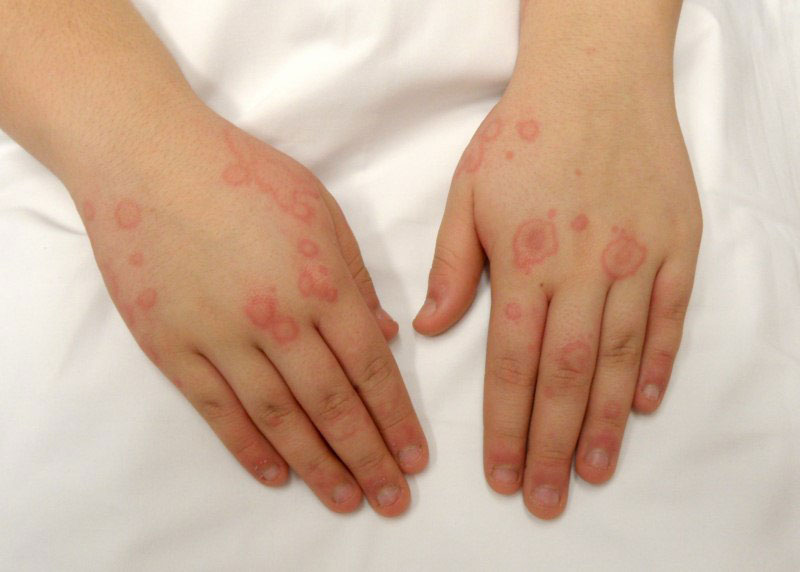
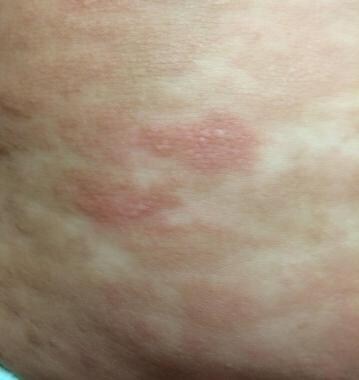
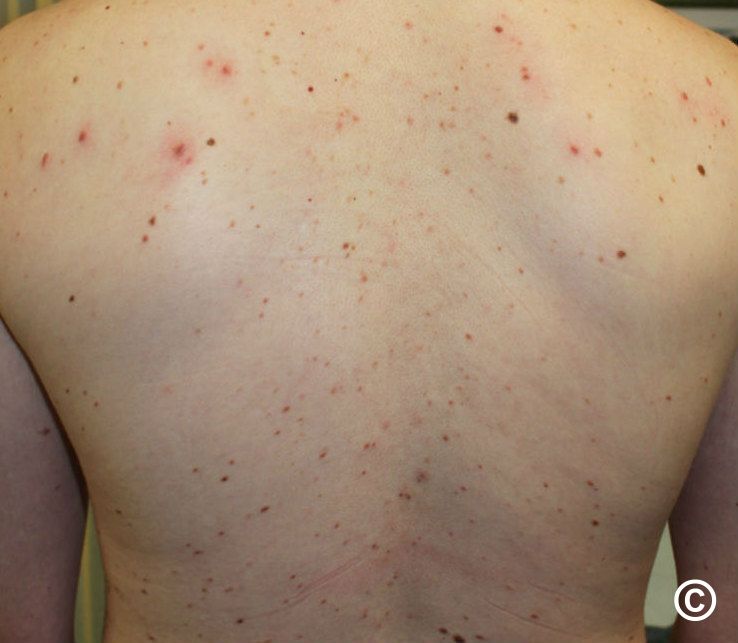
Your child's gp or skin specialist (dermatologist) may rub the. Cutaneous mastocytosis can be diagnosed by the appearance of the patient’s skin and confirmed by counting the number of mast cells appearing in a skin biopsy. Diagnosing mastocytosis, a physical examination of the skin is the first stage in diagnosing cutaneous mastocytosis.
To diagnose mastocytosis and the subtype, a doctor may perform a number of tests. It could take up to 7 years for a patient to be accurately diagnosed with systemic mastocytosis. A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope.
Mastocysotis may be suspected when a doctor sees a person has signs and symptoms of the disease. A blood or urine test may. A rare condition that can be hard to diagnose.
Signs and symptoms of systemic mastocytosis depend on the part of the body affected by excessive mast cells. Your doctor removes a sample of. Diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis per who diagnostic criteria requires presence of the major criterion and at least one minor criterion, or when ≥3 minor criteria are present major criterion.
Patients are often referred to different specialists, such. Cutaneous mastocytosis is the most common presentation of. These tests may include a physical exam, blood and/or urine tests, and biopsies.
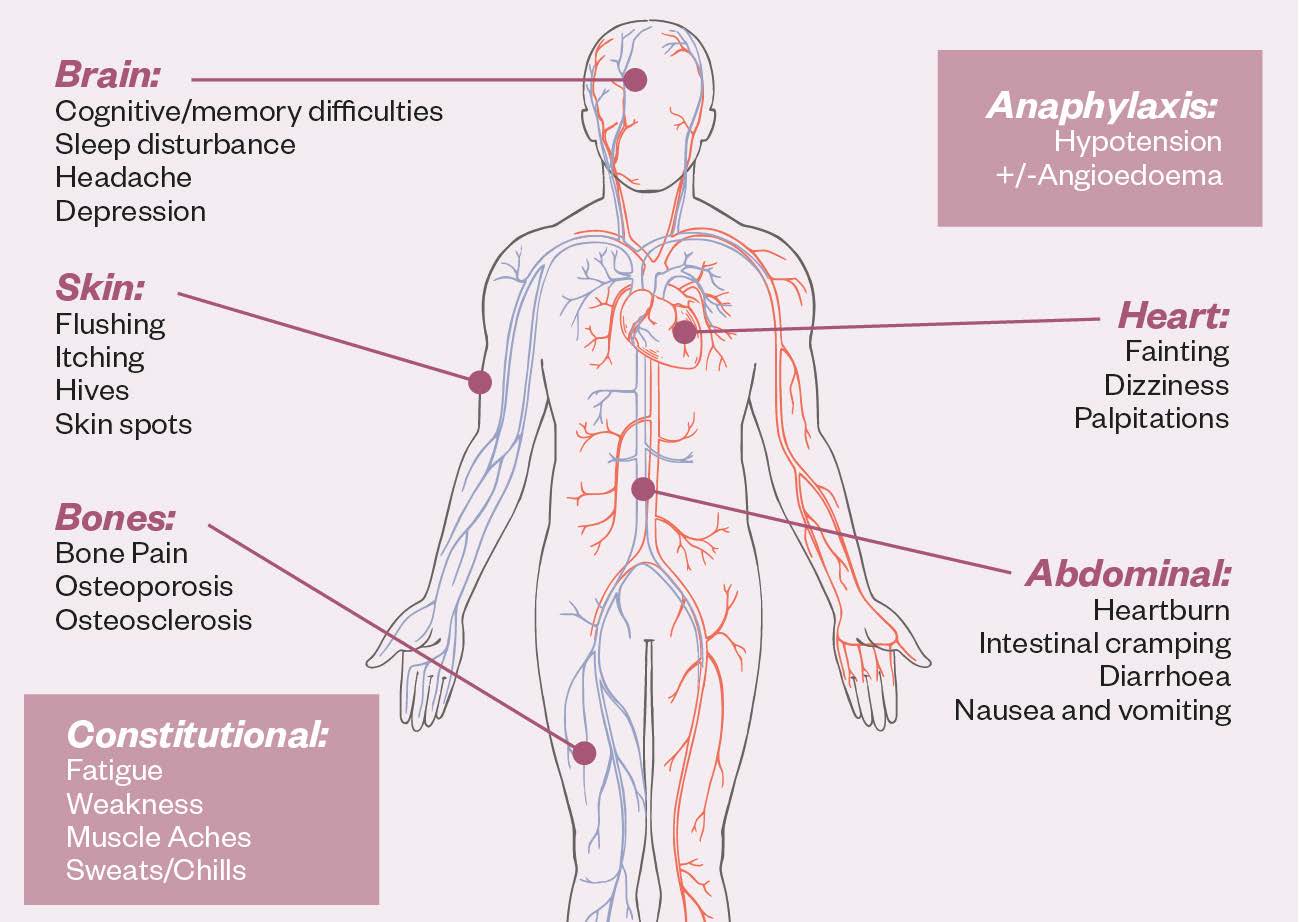

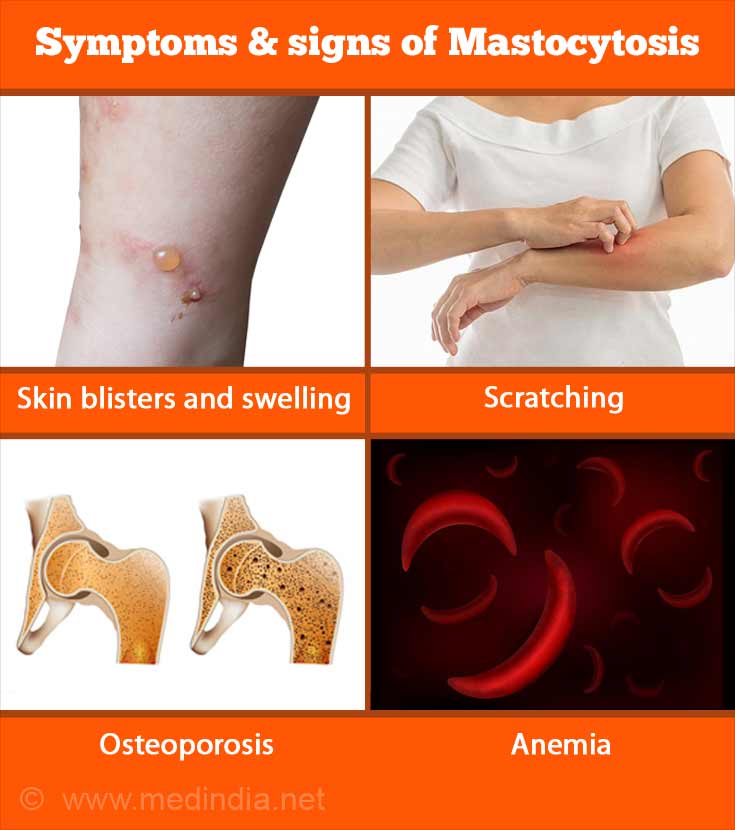

/mast-cell-activation-overview-4583920_final-e0d23ecb82b44e01a6e8ae3536571c76.png)